Course design and quality has a significant impact on student success in an Folio-enhanced course. The following eight indicators are recommended guidelines when designing or reviewing a Folio supported course.
- Design
- Organization
- Clarity
- Accessibility
- Instructor-Interaction
- Peer-Interaction
- Content-Interaction
- Richness
The following list provides Indicator descriptions and indicator examples:
Design
The course’s design should include the following:
- Specific and measurable learning objectives
- Alignment to assessments and learning activities
- Authentic real-world experiences
Organization
- Easy to navigate
- Logical and consistent format
- Alignment between topics and subtopics
- Manageable sections
Organization Examples
- Course is organized with sequential modules.
- Lecture items are appropriately chunked
- Activity items are included in module
- Students do not have to navigate to menus in order to complete activities
- Capstone/Group project items are included in “weekly” modules
Course Organization
Organize courses into sequential modules
| Met | Not Met |
| Sequential Modules | Grouped Modules (Avoid) |
 |  |
| Course journey is clearly presented. | Course journey is not conveyed. |
Met
Sequential modules provide students with a continual understanding of where they are while progressing through a course. Sequential modules guide students through the journey of the course.
Not Met
Grouped or “bucket” modules lead students through excessive clicking and scrolling through disconnected content. Grouped modules hinder students from seeing their journey in a course.
Module Items
Include all module related items in module
| Met | Not Met |
| Activity Items in Module | Activity Items only in menus |
 |  |
| Shows a connection (or alignment) between content and activities. | Content and activities are not presented as being connected to each other. |
Met
All items related to a learning modules should be included in the module. All content pages, discussions, quizzes, assignments, and other activities should be presented to students in one location. This allows students to better plan for the scope of work and see what items need to be completed.
Not Met
Omitting activity items, such as discussions, quizzes, and assignments the related learning module causes excessive navigation and searching. This can lead to inadvertent incompletions of learning activities and assessments.
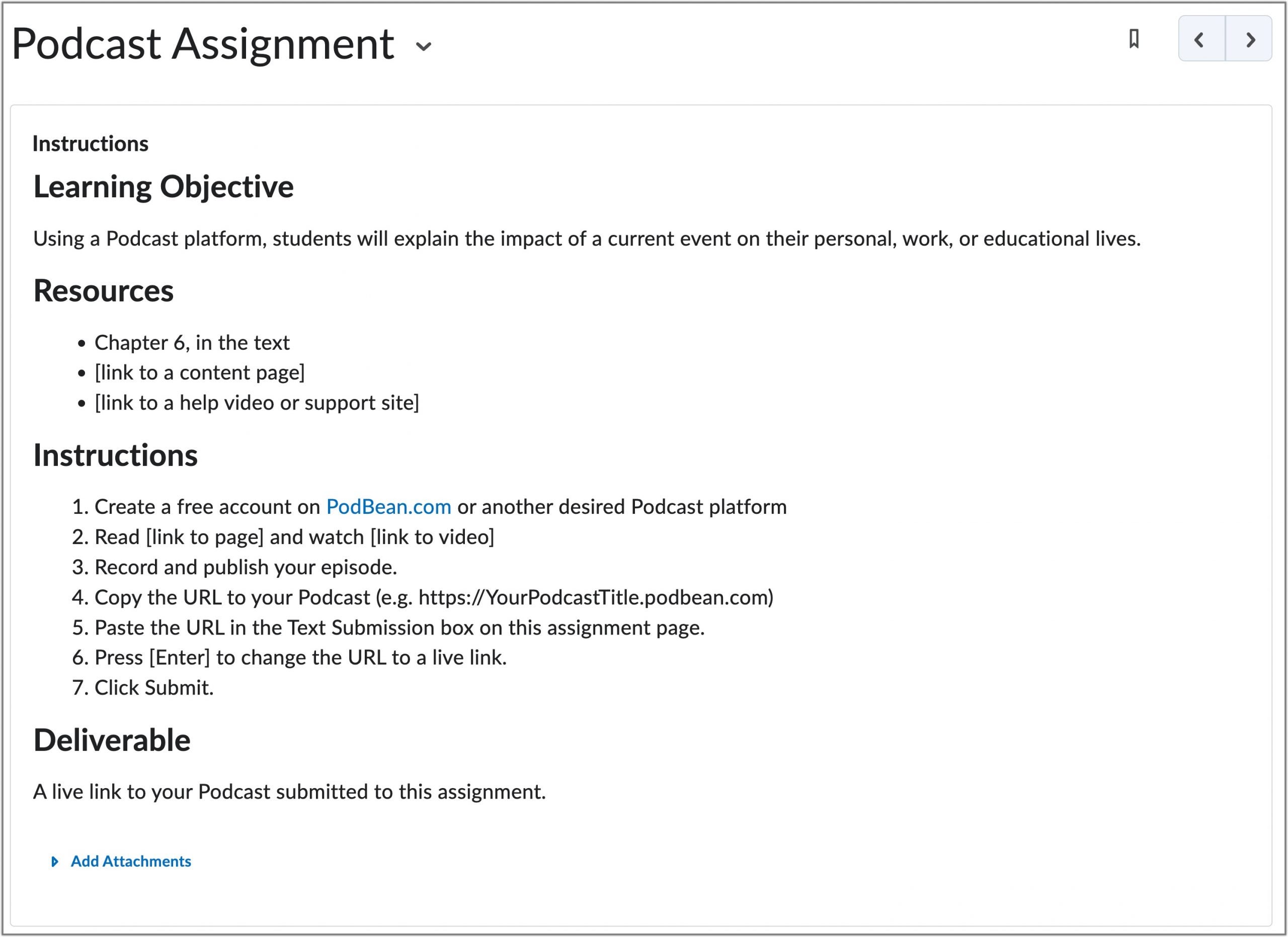
Clarity and Content
Present instructions in sequential order using numbered lists
| Met | Not Met |
| Instructions presented with numbered lists | Instructions presented in paragraphs |
| 1. Develop an idea for your Podcast 2. Download a recommended Podcasting app. 3. Record your Podcast to your mobile device. | Develop an idea for your Podcast. Download a recommended Podcasting app. Record your Podcast to your mobile device. |
| Easily shows next step. Useful for pacing or to mitigate interruptions. | Causes continual review of the paragraph to move to next step. |
Met
Instructions written in sequential order using numbered lists allow students to see progress through the assignment. It is recommend to start each step with a verb.
Not Met
Instructions written in paragraph form causes continuous review to see the next step. If paragraphs are used in instructions, then the should be placed in the beginning as overview statements.
Clarity
- Manage student expectations
- Provide orientation to the course
- Illustrate alignment of objectives, assessments, and activities
- Clear instructions and directions
- Description of grading and assessment plan
Clarity Examples
- Instructions are written in sequential order using numbered list format rather than paragraph format.
- Rubrics are included when applicable.
- Headings are properly used.
- Instructions appear on OR are linked in activity’s description.
Clarity in Folio
| Met | Not Met |
| Instructions written in sequential order using numbered lists allow students to see progress through the assignment. It is recommend to start each step with a verb. | Instructions written in paragraph form causes continuous review to see the next step. If used, paragraphs in instructions should be used in the beginning as overview statements. |
 | |
| Easily shows next step. Useful for pacing or to mitigate interruptions. | Causes continual review of the paragraph to move to next step. |
Accessibility
- Reduce barriers to students by following accessibility guidelines for video captions, image alt-text, and screen-reader friendliness in materials
Accessibility Examples
- Videos are properly captioned with high accuracy, capitalization, punctuation.
- No accessibility Errors appear using Folio’s accessibility checker.
- No objective accessibility Warnings appear when using Foio’s accessibility checker. (contrast, list items).
- Few subjective accessibility Warnings appear when using Folio’s accessibility checker.
Instructor-Interaction
- Express interest in student learning
- Actively participate in discussions
- Facilitate learning and peer interaction
- Expand students’ thoughts and knowledge provide new prompts and additional content
- Provide timely and detailed feedback on assessments and student inquiries
Instructor-Interaction Examples
- Weekly overview videos
- Instructor-created lectured videos
- Facilitates discussion posts with replies
- Completes grading within a timeframe to allow students to reflect on feedback prior to next major assessment.
Peer-Interaction
- Facilitate active learning through frequent peer involvement and meaningful collaborative work
- Provide opportunities and technologies available for students to learn from each other.
Peer-Interaction Examples
- Provides discussion assignments
- Encourages peer responses in Q&A areas.
- Uses Peer-to-peer tools such as Perusall
- Creates group or team projects that utilize collaborative tools such as Google Docs or Padlet.
Content Interaction
- Strategically enhance the student interaction with accessible and interactive content
- Support dialogue, critical reflection and analysis, and real-world applications of the content
- Provide materials that are current, rich, and sufficient in breadth and depth
- Identify important topics and provide context
Richness
Provide richness in learning materials and activities, support and instructions, instructor interactions, and tools and media.
Richness Examples
- Content Videos
- Relevant images
- Interactive tools such as Perusall, YuJa, Nearpod, Padlet, or Thinglink.
Adapted from the National Research Center for Distance Education and Technological Advancements (DETA) at the University of Wisconsin – Milwaukee, https://detaresearch.org/research-support/teaching-resources/
